Thermal Science and Energy|Research|
Thermal Science and Energy Laboratory, Department of Energy and Environmental Engineering
Balancing energy supply with demand and enhancing environmental protection are still big challenges for our society. In our laboratory, combustion, and heat and mass transfer phenomena are the major topics based on thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and thermochemistry to realize clean energy and low-carbon technologies. A complex physics in which the turbulence and the chemistry interact each other is investigated to clarify the characteristics, to build the mathematical models, and to perform the numerical simulation of such a multiscale and multiphysics phenomena among gas, solid, and liquid three phases.
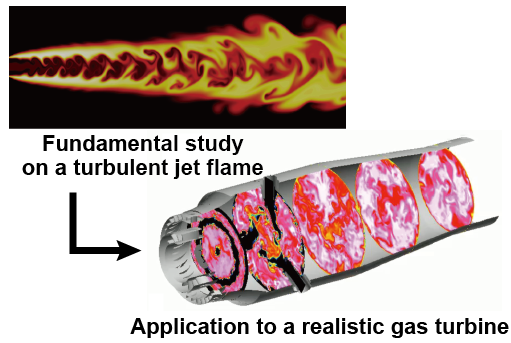
Modeling and simulation of turbulent combustion
Turbulent combustion is utilized in almost industrial applications such as aircraft engines, automotive engines, power generation gas turbines, and so on. Since the turbulent combustion in which the turbulence - chemistry interaction is taking place shows very complex behavior, it is important and essential to deeply understand the physics underlying in the turbulent flame in order to realize the innovative combustion technologies. In this study, a turbulent combustion model in which the detailed elementary reactions can be considered and the computational cost is low is investigated.
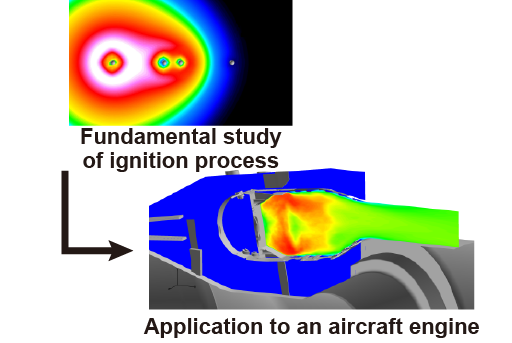
Modeling and simulation of multiphase combustion
Spray combustion that is one of the multiphase combustion phenomena is utilized in aircraft engines and Diesel engines. Since spray combustion is a complex phenomenon in which dispersion of the liquid fuel droplets, their evaporation, and chemical reaction take place interactively at the same time, the underlying physics governing these processes has not been well understood. In this study, to understand the spray combustion and to model these complex physics a numerical simulation with a detailed chemistry is performed and the model developed here is applied to a practical scale combustor.
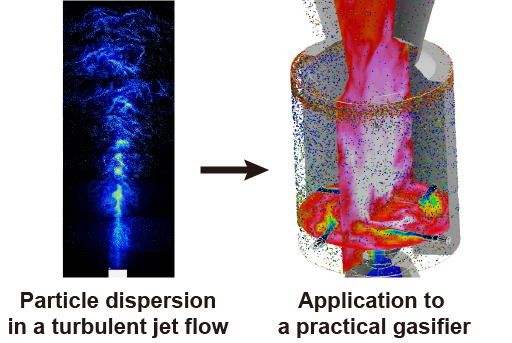
Gasification technology for a solid material
It is possible to design a CO2 ZERO/Negative emission power generation system with firing solid fuel by employing a gasification technology. It is essential to produce high quality synthetic gas in a gasifier by promoting the solid material conversion in the turbulent reacting flow. In this study, we clarify the solid fuel particles motion and chemistry to develop a numerical simulation technique to design a practical scale plant.
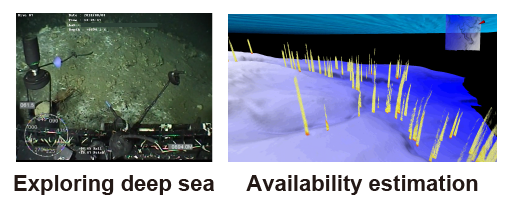
Utilization technology of methane hydrate
A tremendous amount of methane hydrate has been recently explored on the surface of the seafloor near Japan's coast. An efficiently mining and recovery technology is being developed by the national project from the energy security's point of view. In this study, the behavior of methane hydrate particles and the methane gas bubbles within the process unit is investigated to develop the mining and recovery plant.